DHA is known to be important for normal brain function and therefore it is reported that in persons with low dietary consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), the supplementation with DHA might improve cognitive function.
This study was performed to evaluate the effects of DHA supplementation on cognitive performance in healthy young adults.
Cognitive performance (memory, attention and reaction time {RT}) by using computerized cognitive test battery
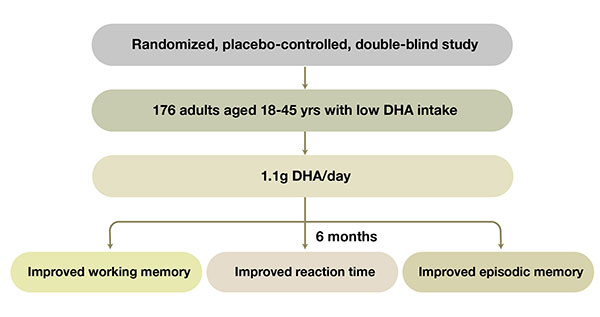
DHA supplementation significantly improved memory and reaction time in healthy young adults whose diets were low in DHA.
Stonehouse W, Conlon CA, Podd J, et al. DHA supplementation improved both memory and reaction time in healthy young adults: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97(5):1134-1143.
DHA, the principle omega-3 fatty acid in brain, plays a very important role in neural function. Reductions in plasma DHA levels has been associated with cognitive decline in elderly and Alzheimer’s patients.
This study was performed to assess the beneficial effects of DHA in improving cognitive function in healthy older adults with age-related cognitive decline (ARCD).
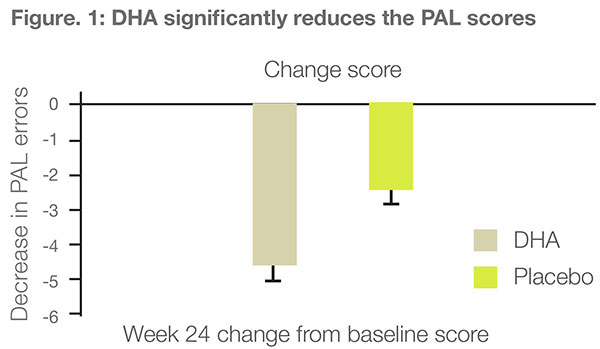
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical study.
485 subjects with ≥ 55 y of age with Mini-Mental State Examination >26 and a Logical Memory (Wechsler Memory Scale III) baseline score ≥ 1 standard were enrolled.
900 mg of DHA or placebo per day respectively.
24 weeks.
CANTAB Paired Associate Learning (PAL), a visuospatial learning and memory test
DHA supplementation is significantly beneficial in improving learning and memory function in ARCD patients.
Mauro YK, McCarthy D, Hall EB, et al. Results of the MIDAS trial: Effects of docosahexaenoic acid on physiological and safety parameters in age-related cognitive decline. Alzheimers Dement. 2009; 5(4):P84.
It is found that the depressive symptoms may augment the risk of progression from mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to dementia. Consumption of n-3 PUFA may relieve both depression and cognitive decline.
The aim of this study was to investigate the beneficial effects of omega-3 PUFAs on depressive symptoms, quality of life (QOL) and cognition in elderly people with MCI.
Double-blind, randomized controlled trial.
50 people aged >65 years with MCI were enrolled into the study.
6 months
| Groups | Intervention | Number of subjects (n=) |
|---|---|---|
| Rich in DHA | 1.55g DHA + 0.40 g EPA/day | 18 |
| Rich in EPA | 1.67g EPA + 0.16g DHA/day | 17 |
| Linoleic Acid(LA) | 2.2 LA g/day | 15 |
DHA supplementation benefited mental health in older people with MCI
Omega-3 PUFAs supplement significantly reduced the depressive symptoms and altered the risk of progression to dementia.
Sinn N, Milte CM, Street SJ, et al. Effects of n-3 fatty acids, EPA vs. DHA, on depressive symptoms, quality of life, memory and executive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: a 6-month randomized controlled trial.Br J Nutr. 2012;107(11) : 1682169
Docosahexaenoic acid is the major fatty acid found in the brain and several researches have shown that the DHA content in the brain and plasma is reduced in patients with dementia.
The aim of this study was to assess the association between plasma phosphatidylcholine (PC) DHA concentration and risk of developing dementia.
A prospective follow-up study.
899 men and women of median age 76 years without dementia at the baseline.
A mean follow-up of 9.1 years was done to assess the development of all-cause dementia and Alzheimer disease (AD).
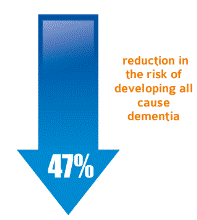
It was concluded that the highest quartile of PC DHA levels were associated with a significant reduction of developing all cause dementia
Schaefer EJ, Bongard V, Beiser AS, et al. Plasma phosphatidylcholine docosahexaenoic acid content and risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease: the Framingham Heart Study. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(11):1545-1550.
DHA is found in the phospholipid fraction of the brain and is a major polyunsaturated fatty acid of the brain .It was not known whether supplemental DHA has any effects on the higher functions of the brain in young adults. So, this study was conducted to assess the efficacy of DHA in preventing aggression in adults.
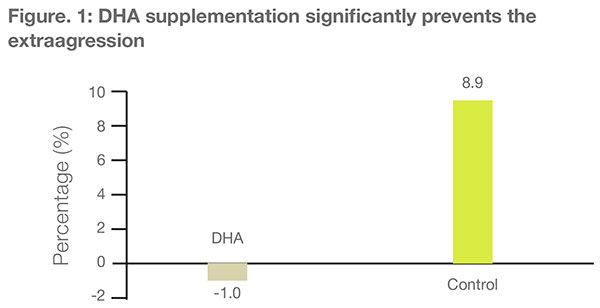
A placebo-controlled double-blind study.
41 young adults.
1.5-1.8 g of DHA daily (n =22) or control oil (n =19).
3 months
The stability in extraggression percentage in the DHA group indicates aggression-controlling effects of DHA
DHA supplementation significantly prevents extraggression in young adults
Hamazaki T, Sawazaki S, Itomura M, et al. The effect of docosahexaenoic acid on aggression in young adults. A placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(4):1129-1133